Model Deployment
Created: 2023-02-23 10:58
#quicknote
Process of making the model available in prodution.
Challenges:
- reliability ->rebustness against errors
- reusability -> how easy can be used in other projects
- maintainability -> how easy is to maintain the product in future
- flexibility -> how easy is to modify (add/remove) it
- reproducibility -> can I reproduce results?
Pipeline:
- Obtain data -> Cloud, DB, Third party API;
- Work on the data -> feature engineering;
- Training;
- Scoring;
- Predictions
Enviroments:
- Research -> test of models and parameters;
- production -> real-time setting available for business use
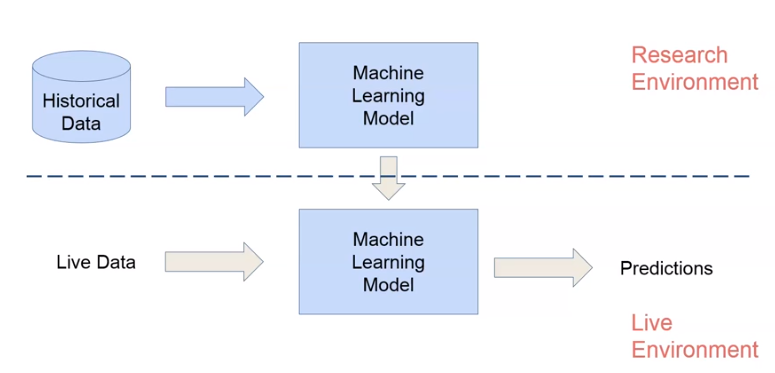
We have different pipelines for research and production environments, but given the same data we should have the same predictions in both scenarios.
NOTE: witout the ability to replicate prior results, it is difficult to determine if a new model is truly better than the previous one.
To guarantee reproducibility, we need to ensure that all the steps in the pipelines are reproducible, i.e. they give the same results if the data is the same.
The most challenging step, if we are concerned about reproducibility, is Data Gathering. Problems: training dataset can not be reproduced, DBs are constantly updated and overwritten, order of data while loading is random (SQL); solutions: save snapshot of training data (but we could have conflicts with GDPR and we could have problems with big data), design sata surces with accurate timestamps (ok but gib efforts).
During Feature Creation we could also have problems: when replacing missing data with random extracted values, when removing labels based on percentages of observations etc. Solutions: feature generation code should be tracked under version control, many of the geerated values depend on the data used for training (so endure data is reproducibe), set the seed for the random samples.
Model Training: ML models rely on randomness for training and they work with arrays agnostic to feature names -> record order of the features, applied feature transformations, hyperparameters, structure of the ensemble (if there is one), and always set a seed.
Model Deployment-> problems: a feature is not always available in the live environment, different programming languages or software are used. Solutions: software versions should match exactly, so use containers and understand how the model will be integrated with otehr systems (before building the model).
A solution for Reproducibility is to use Open Source tools, these are already tested and we chould guarantee the same results if we use the same tools both in the research and the production stages.
Resources
- Reproducible ML
- The ML Reproducibility Crisis
- 6 Motivations for consuming or publishing open source software
- How to build and deploy a reproducible ML pipeline
- Building a reproducible ML pipeline
Tags
#ml #course